%%capture
!pip install kornia
!pip install kornia-rsRandom Mosaic Augmentation
Basic
2D
Data augmentation
kornia.augmentation
In this tutorial we will show how we can quickly perform mosaicing using the features provided by the
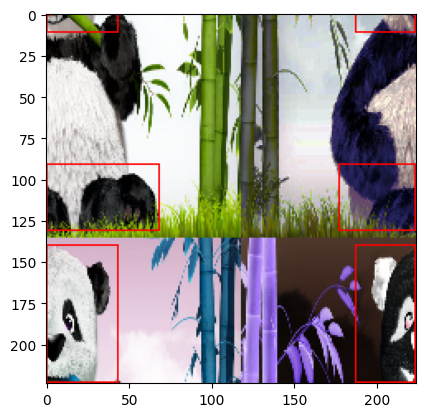
kornia.augmentation.RandomMosaic API. Mosaicing means taking several input images and combine their random crops into mosaic.
Install and get data
We install Kornia and some dependencies, and download a simple data sample
import io
import requests
def download_image(url: str, filename: str = "") -> str:
filename = url.split("/")[-1] if len(filename) == 0 else filename
# Download
bytesio = io.BytesIO(requests.get(url).content)
# Save file
with open(filename, "wb") as outfile:
outfile.write(bytesio.getbuffer())
return filename
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kornia/data/main/panda.jpg"
download_image(url)'panda.jpg'import kornia as K
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def plot(img, box):
img_vis = img.clone()
img_vis = K.utils.draw_rectangle(img_vis, box, color=torch.tensor([255, 0, 0]))
plt.imshow(K.tensor_to_image(img_vis))
plt.show()img1 = K.io.load_image("panda.jpg", K.io.ImageLoadType.RGB32)
img2 = K.augmentation.RandomEqualize(p=1.0, keepdim=True)(img1)
img3 = K.augmentation.RandomInvert(p=1.0, keepdim=True)(img1)
img4 = K.augmentation.RandomChannelShuffle(p=1.0, keepdim=True)(img1)
plt.figure(figsize=(21, 9))
plt.imshow(K.tensor_to_image(torch.cat([img1, img2, img3, img4], dim=-1)))
plt.show()
import kornia as K
import torch
from kornia.augmentation import RandomMosaic
x = K.core.concatenate(
[
K.geometry.resize(img1[None], (224, 224)),
K.geometry.resize(img2[None], (224, 224)),
K.geometry.resize(img3[None], (224, 224)),
K.geometry.resize(img4[None], (224, 224)),
]
)
boxes = torch.tensor(
[
[
[70.0, 5, 150, 100], # head
[60, 180, 175, 220], # feet
]
]
).repeat(4, 1, 1)
aug = RandomMosaic(
(224, 224), mosaic_grid=(2, 2), start_ratio_range=(0.3, 0.5), p=1.0, min_bbox_size=300, data_keys=["input", "bbox_xyxy"]
)
y, y1 = aug(x, boxes)
plot(y[:1], y1[:1])Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers).